What is Fiber to the Home (FTTH)?
Fiber to the Home, abbreviated as FTTH, is a transmission method in fiber optic communication. As the name implies, it involves directly connecting fiber optic cables to user terminals. FTTH is a type of access method within the broader category of FTTx.
FTTx (Fiber to the X):
FTTx is a collective term encompassing various application types in broadband optical access networks. The “X” has multiple variants, such as Fiber to the Building (FTTB), Fiber to the Cabinet (FTTCab), Fiber to the Curb (FTTC), Fiber to the Desk (FTTD), Fiber to the Home (FTTH), Fiber to the Premises (FTTP), Fiber to the Office (FTTO), Fiber to the User (FTTu), and others.
The FTTx technology spans from the central office equipment in regional telecommunication facilities to user terminal devices. This includes Optical Line Terminal (OLT), Optical Network Unit (ONU), and Optical Network Terminal (ONT) in the optical line network.
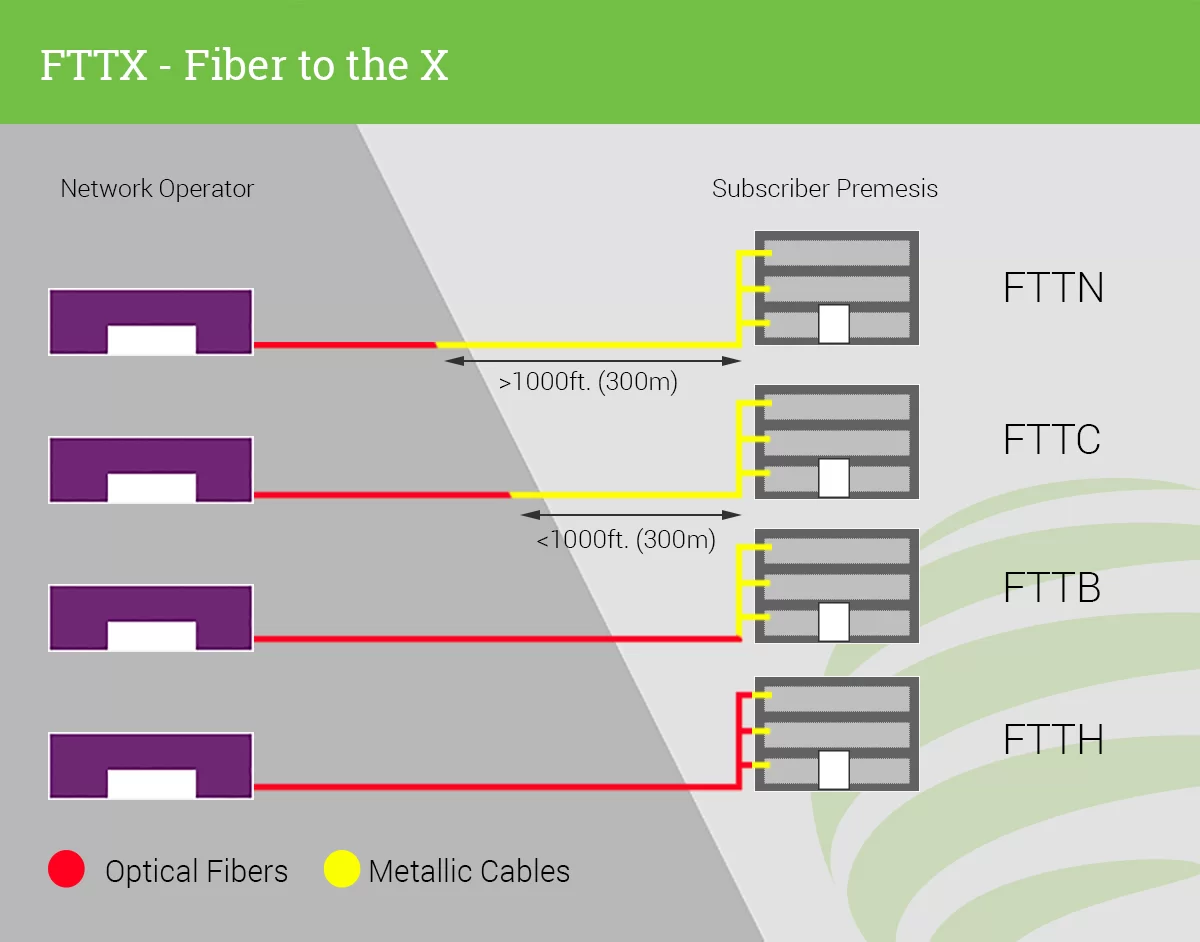
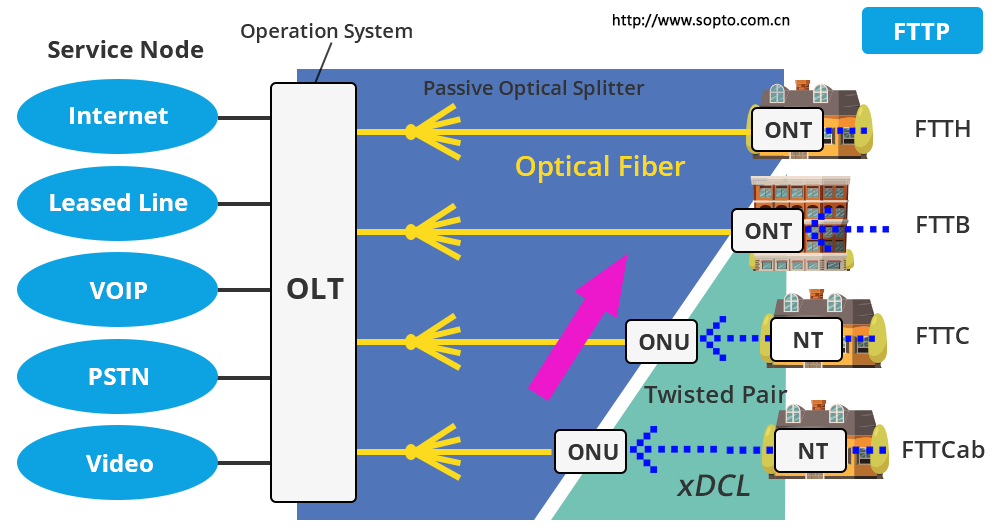
From the diagram, it can be observed that FTTH is entirely connected to the terminal via a fiber optic network, and the terminal connected to it is called the Optical Network Terminal (ONT). In the case of FTTB or FTTC, they are connected to buildings or curbs through a fiber optic network, and then connected to terminals via copper twisted-pair networks or wireless connections. The end devices in the fiber optic network are referred to as Optical Network Units (ONU), which are connected to the Network Terminal (NT) through copper twisted-pair networks or wireless connections.
FTTCab is similar to FTTC, with the difference being that its ONU is located in the telecommunication cabinet. FTTB, FTTC, and FTTCab in the diagram all fall under the category of “partial” fiber to the home, meaning that the fiber is not directly connected to the end user but reaches near the end user and then connects to the end user via twisted-pair networks.
In FTTCab, the ONU in the telecommunication cabinet is typically located 1000 to 2000 meters away from the end user. In this scenario, one ONU unit can support approximately 500 end users. In FTTC, the ONU is closer to the end user, ranging from 200 to 1000 meters, and can support 8 to 32 end users. The network between OLT and ONT/ONU is known as the Optical Distribution Network (ODN), with a distance of up to 20km, as shown in the diagram.
FTTH Related Terms:
FTTH (Fiber to the Home):
FTTB (Fiber to the Building):
FTTO (Fiber to the Office):
FTTC (Fiber to the Curb):
ODN (Optical Distribution Network):
OLT (Optical Line Terminal):
ONU (Optical Network Unit):
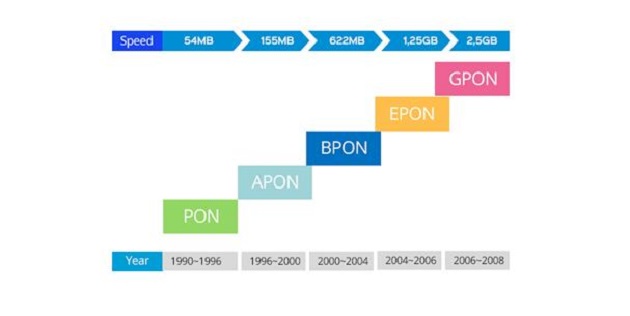
PON (Passive Optical Network):
EPON (Ethernet Passive Optical Network):
GPON (Gigabit-capable Passive Optical Network):
NT (Network Terminator):
ONT (Optical Network Terminator):
P2MP (Point to Multipoint):
CO (Center Office):
FTTH Market Situation:
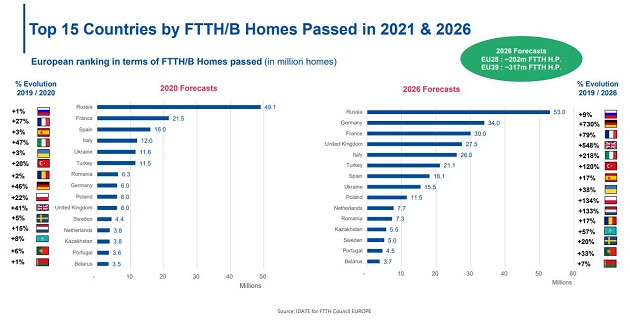
At the 2020 FTTH Virtual Conference on December 3, the 2020~2026 FTTH market forecast data compiled by IDATE and FTTH Council Europe indicated that, by 2026, the number of subscribers in 27+ EU and UK countries will further increase to approximately 148 million. The number of subscribers in 38+ EU and UK countries is expected to reach around 208 million. The coverage of FTTH/B is projected to reach 73.3% in 2026, a significant increase compared to 23.4% in 2012.
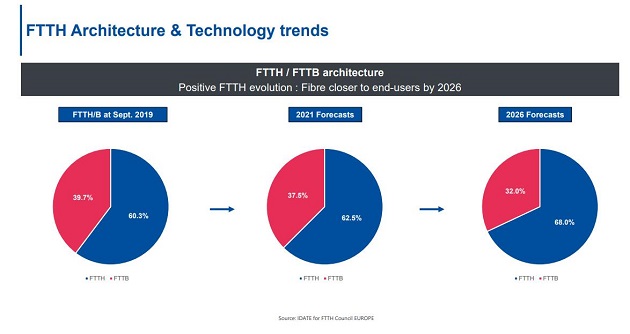
According to the forecast, the number of users in some countries will experience a substantial increase compared to 2019. For example, Germany is expected to grow by +730%, the UK by +548%, and Italy by +218%. In terms of country rankings, Russia may continue to lead, but Germany is expected to rise to second place in 2026, whereas it was eighth in the 2020 ranking.
Technical Development of FTTH:
As an access technology, FTTH has gained recognition and its technology has matured. There are two commonly used fiber optic access technologies in FTTH: Point-to-Point (P2P) and Point-to-Multipoint (P2MP, Passive Optical Network – PON).
P2P (Point-to-Point): P2P is a peer-to-peer network technology that allows direct communication between two users without public IP addresses.
PON (Passive Optical Network): PON is a passive optical network, indicating that there are no active devices in the Optical Distribution Network (ODN) between the Optical Line Terminal (OLT) and the Optical Network Unit (ONU). It relies solely on fiber optics and passive components. PON primarily adopts a point-to-multipoint network structure and is the key technology for achieving FTTB/FTTH.
PON technology can be divided into narrowband PON technology for narrowband TDM business access, Broadband PON (BPON) based on ATM transmission, Ethernet PON (EPON) based on Ethernet packet transmission, and GPON technology that integrates ATM/Ethernet/TDM comprehensively for broadband access. All three of these technologies are currently commercially deployed PON technologies that achieve FTTX.